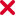
Geometria Analítica: Parábola
1. Legenda
2. Equação da parábola (forma geral)
y^2=2px
\end{align}
\begin{align}
& \text{Equation of the directrix: $x=-\frac{p}{2}$}
\\
& \text{Coordinates of the focus: $F \left( \frac{p}{2},0 \right)$}
\\
& \text{Coordinates of the vertex: $M(0,0)$}
3. Forma geral
Ax^2+Bxy+Cy^2+Dx+Ey+F=0 \qquad B^2-4AC = 0
4.
y=ax^2, p=\frac{1}{2a}
\end{align}
\begin{align}
& \text{Equation of the directrix: $y=-\frac{p}{2}$ }
\\
& \text{Coordinates of the focus: $F \left( 0, \frac{p}{2} \right)$ }
\\
& \text{Coordinates of the vertex: $M(0,0)$ }
5. Forma geral com eixos paralelo ao eixo $y$
& Ax^2+Dx+Ey+F=0 \qquad (A, E nonzero)
\\
& y=ax^2+bx+c, p=\frac{1}{2a}
\end{align}
\begin{align}
& \text{Equation of the directrix: $y=y_{0}-\frac{p}{2}$ }
\\
& \text{Coordinates of the focus: $F \left( x_{0}, y_{0} + \frac{p}{2} \right)$ }
\\
& \text{Coordinates of the vertex: $x_{0}=-\frac{b}{2a}$, $y_{0}=ax_{0}^2+bx_{0}+c=\frac{4ac-b^2}{4a}$ }